- A+
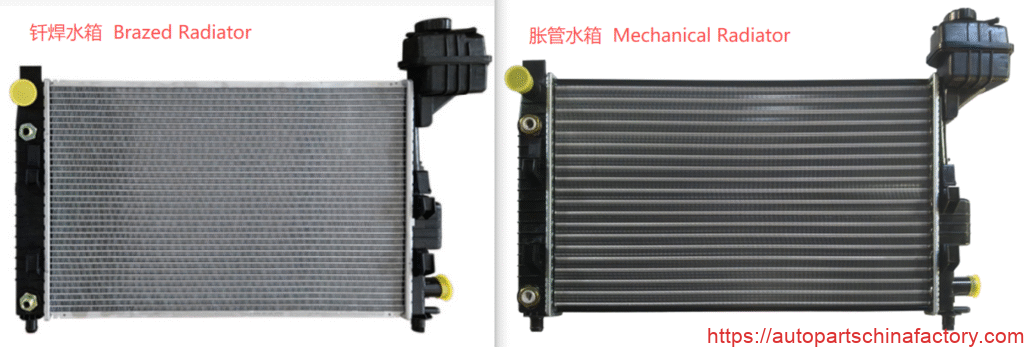
The engine is the heart of a car, and the radiator is its "air conditioner." It is crucial for maintaining stable engine temperature. The mainstream radiator technologies currently on the market are mainly divided into two categories: the Mechanical Radiator and the Brazed Radiator.
What are the differences between these two types of radiators? Which one is better suited for your vehicle or your business needs?
This article will provide an in-depth analysis from the perspectives of product attributes, performance, lifespan, and global trends.
🛠️ Product Attribute Comparison: Mechanical vs. Brazed
| Attribute | Mechanical Radiator | Brazed Radiator |
| Appearance/Structure | Connected using a mechanical expansion process; the contact point between the tubes and fins often has a slight crimp or bulge. Side tanks/end plates are typically plastic or sealed with rezin contalar. | Connected using the brazing process; tubes, fins, and tanks are integrated into one piece (metallurgical bond). The structure is tight, and seams are smooth. Mostly all-aluminum or all-copper structures. |
| Joining Material | Rubber gaskets, plastic/nylon end tanks (PA66+GF). | Brazing alloy (E.G., aluminum-silicon alloy), achieving a metallurgical bond. No gaskets. |
| Primary Material | Aluminum core + Plastic End Tanks (PA66+GF). | Aluminum core + Plastic End Tanks ; All-Aluminum or All-Copper. |
| Manufacturing Process | Mechanical expansion, where tubes expand to press against fins; tanks are secured with bolts/clamps. | High-temperature vacuum or atmosphere brazing, fusing the core components together. |
| Service Life | Gaskets are prone to aging and plastic tanks can become brittle, leading to a relatively shorter lifespan (5-8 years or less). | High structural integrity, strong pressure resistance, good vibration resistance, leading to a relatively longer lifespan (8-15 years or more). |
| Cooling Performance | Heat transfer between fins and tubes is not a metallurgical bond, resulting in slightly lower efficiency; performance is relatively moderate. | Brazed connection provides excellent thermal conductivity and high heat transfer efficiency; cooling performance is superior. |
| Pressure Endurance | Limited by the plastic tanks and gaskets, pressure resistance is weaker. | All-metal structure, offering very strong pressure resistance, suitable for high-load engines. |
| Weight | Adətən lighter than all-aluminum brazed radiators due to the plastic components. | All-metal, relatively heavier, but new thin-walled brazed radiators have significantly reduced weight. |
| Repairability | Easy to disassemble and replace tanks or gaskets; repairability is relatively good. | Damage often requires complete replacement; difficult to repair (requires professional brazing). |
| Price | Lower production cost, typically more affordable. | Complex manufacturing process and higher material costs result in a relatively higher price. |
📈 Global Trends and Market Analysis
The global choice of radiators by automakers and the aftermarket reflects a trade-off between cost, performance, and lifespan:
1. Market Position of Mechanical Radiators

- Popular Regions/Vehicle Types: Due to their advantages of low cost and lightweight design, mechanical radiators dominate the entry-to-mid-level economy car and passenger vehicle market. They remain the mainstream choice in most Original Equipment (OE) markets across Asia, Europe, and North America.
- Reason for Popularity: The introduction of plastic tanks has significantly lowered both cost and weight, meeting the needs of most cars for cost control and fuel efficiency. Their cooling performance is sufficient for vehicles operating under relatively moderate engine conditions.
2. Market Position of Brazed Radiators

- Popular Regions/Vehicle Types: Brazed radiators are primarily used in high-performance sports cars, luxury vehicles, heavy-duty trucks, construction machinery, and the aftermarket for high-load or modified vehicles.
- Reason for Popularity: All-aluminum brazed radiators offer outstanding cooling efficiency, excellent structural strength, and high-pressure resistance. Their stability, reliability, and long lifespan make them indispensable under high thermal loads and severe operating conditions (such as off-roading, racing, or heavy hauling).
- All-copper/brass brazed radiators (popular in older models) are still favored by some repair markets for their superior repairability and thermal conductivity.
💡 Summary of Similarities and Differences
Similarities
- Basic Function: Both circulate coolant to use air convection to dissipate excess heat generated by the engine, ensuring the engine operates within the optimal temperature range.
- Core Structure: Both include the three essential components: Tubes, Fins, and Tanklar.
- Main Material: Modern automotive radiators are predominantly made of aluminum due to its lightweight and good thermal conductivity.
Differences
| Xüsusiyyət | Advantage of Mechanical Radiator | Advantage of Brazed Radiator |
| Cost/Price | Affordable price, high cost-effectiveness. | Though higher priced, a longer lifespan and better performance offer better long-term value. |
| Structure/Joints | Convenient for assembly and high-volume mass production. | All-metal metallurgical bond, the structure is seamless, robust, and corrosion-resistant. |
| Performance/Life | Clear advantage in lightweight design. | Higher cooling efficiency, more resistant to high pressure, and a longer service life. |
Rəy: How to Make Your Choice?
Choosing between a mechanical and a brazed radiator depends on your needs and budget:
- ✅ Choose the Mechanical Radiator if:
- You are looking for the lowest procurement cost.
- Your vehicle is an entry-to-mid-range commuter car, driven in mild conditions, with no extreme cooling requirements.
- You require a lightweight solution.
- ✅ Choose the Brazed Radiator if:
- Your vehicle is a high-performance, turbocharged, heavy-duty, or modified model.
- You use your vehicle in high-load, off-road, or racing environments.
- You require the longest service life and best cooling performance.
Regardless of the type of radiator you choose, regular coolant replacement and radiator inspection are key to ensuring the long-term health of your engine.