- A+
當夏天的熱量襲來, there's one unsung hero in your car's air conditioning system that keeps you cool: the automotive condenser. Often mistaken for a radiator, this crucial component plays a vital role in transforming hot refrigerant gas into a cooler liquid, making your cabin a comfortable oasis.
But what exactly is an automotive condenser, how is it made, and where do these essential parts come from? Let's take a closer look.
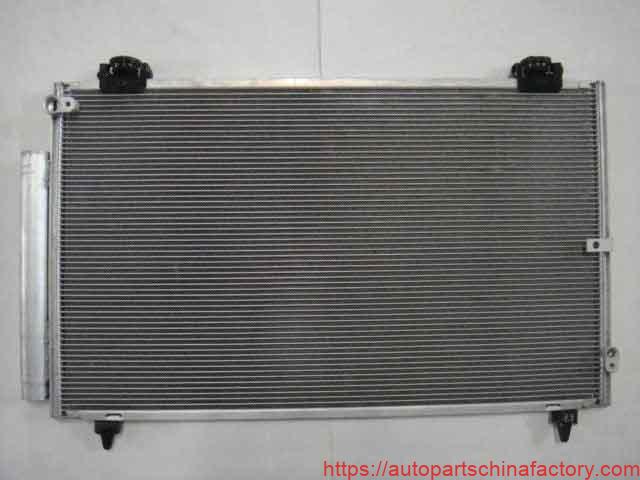

What is an Automotive Condenser and Why is it Essential?
The automotive condenser is a heat exchanger located typically at the front of your vehicle, often in front of the radiator. Its primary function is to dissipate heat from the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant vapor that exits the AC compressor.
Here's a simplified breakdown of its role in your car's AC system:
- Compression: The AC compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, turning it into a hot gas.
- Condensation: This hot gas then flows into the condenser. As air (from the vehicle's movement or a dedicated fan) passes over the condenser's fins and tubes, heat is transferred from the refrigerant to the cooler ambient air. This causes the refrigerant to "condense" and change from a high-pressure gas into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion & 蒸發: The now liquid refrigerant flows to the expansion valve and then to the evaporator, where it rapidly expands and cools, absorbing heat from the cabin air.
- Circulation: The cooled, low-pressure gas then returns to the compressor to restart the cycle.
Without a properly functioning condenser, your car's AC system simply can't cool effectively, leading to a hot and uncomfortable driving experience.
How are Automotive Condensers Manufactured? The Production Process
The manufacturing of automotive condensers is a precise process, typically involving several key stages to ensure efficient heat transfer and durability. Modern condensers largely utilize aluminum due to its excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties.
Here's a general overview of the manufacturing process:

- Core Fabrication:
- Tube Forming: Aluminum sheets are often formed into flattened tubes or "micro-tubes." Modern designs, like parallel flow condensers, utilize multiple parallel passages to maximize surface area for heat exchange.
- Fin Production: Thin, corrugated aluminum fins are precisely cut and shaped. These fins are crucial for increasing the surface area for heat dissipation.
- Assembly of Core: The tubes and fins are meticulously stacked and arranged to create the condenser's core. The arrangement ensures maximum contact between the refrigerant-carrying tubes and the air-facing fins.
- Manifold and Header Attachment: Aluminum manifolds (or headers) are attached to the ends of the core, creating entry and exit points for the refrigerant. These often feature internal baffles to direct the refrigerant flow efficiently through the multiple passages.
- Brazing: This is a critical step where the entire assembly (tubes, 鰭, and manifolds) is heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace with a brazing alloy. The alloy melts and flows into the joints, creating strong, leak-proof bonds between all the components. This process is essential for the integrity of the heat exchanger.
- Leak Testing: After brazing, every condenser undergoes rigorous leak testing to ensure there are no imperfections that could lead to refrigerant leaks. This often involves pressure testing with air or nitrogen, sometimes submerged in water to detect bubbles.
- Drier/Receiver Integration (Optional but Common): Many modern condensers incorporate a receiver-drier or an integrated drier element. This component is responsible for filtering out moisture and debris from the refrigerant, protecting the AC system from damage.
- Final Inspection & Packaging: Condensers are visually inspected for quality, and then carefully packaged for shipment to automotive assembly plants or aftermarket distributors.
Sourcing Your Automotive Condenser: Where Do They Come From?
Sourcing an automotive condenser, whether for a new vehicle or a replacement part, involves understanding the global supply chain. Key players in the automotive parts industry manufacture these components worldwide.
- Original Equipment (OE) Manufacturers: Major automotive component suppliers produce condensers directly for car manufacturers. These are the parts your vehicle came with from the factory. Companies like Valeo, 丹森, 沙, and Mahle are prominent names in this sector.
- Aftermarket Suppliers: A vast network of aftermarket automotive parts manufacturers and distributors provide replacement condensers. These can range from direct OE replacements to more affordable alternatives. When buying an automotive condenser, it's important to consider quality and compatibility. Many aftermarket suppliers source from factories that also produce OE parts, ensuring high standards.
- Global Manufacturing Hubs: The manufacturing of automotive condensers is spread across various regions, often concentrated in countries with strong automotive industries and established manufacturing capabilities.
- Asia: China, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asian nations are significant production hubs, offering both high-volume manufacturing and specialized production.
- Europe: Countries like Germany, France, and Eastern European nations also have a strong presence in automotive component manufacturing, including condensers.
- North America: Mexico and the United States also host significant manufacturing facilities for automotive parts, serving the North American market.
When sourcing auto AC parts, look for reputable suppliers and brands known for quality and reliability. Online marketplaces and specialized automotive parts distributors are common avenues for sourcing.