- A+
When the summer heat hits, there's nothing quite like stepping into a cool, air-conditioned car. But have you ever wondered how that refreshing blast of cold air is actually generated? The unsung hero behind your vehicle's air conditioning system is a crucial component called the evaporator.
In this post, we'll delve into the structure, function, and mechanical principles of the automotive evaporator. We'll also touch upon its supply chain, import factories, and key manufacturers, providing a comprehensive overview for car enthusiasts and industry professionals alike.
What is an Evaporator?
Looking at the images provided , you can see the evaporator is essentially a heat exchanger. It's typically a compact, finned coil made of aluminum, designed to maximize surface area for efficient heat transfer.
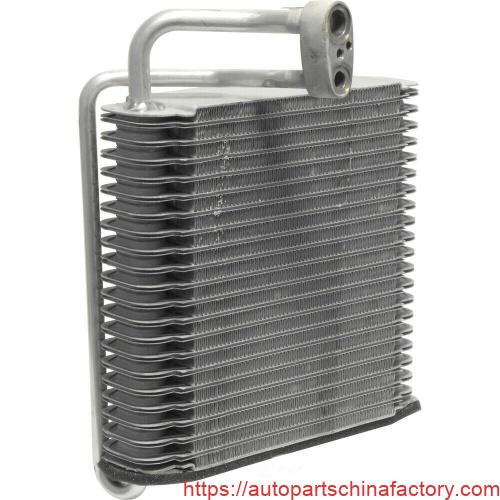

Evaporator Structure:
- Πτερύγια: Numerous thin, corrugated aluminum fins are stacked closely together, creating a large surface area for air to pass through.
- Tubes/Channels: Refrigerant flows through internal tubes or channels that weave through these fins. These are often flat-sided to provide more contact with the fins.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: These are the connection points where refrigerant enters and exits the evaporator. You can clearly see these ports in the provided images.
- Manifolds/Tanks: At either end of the core, manifolds distribute refrigerant evenly into the multiple tubes.
How Does an Evaporator Work? The Mechanical Principle
The evaporator operates on a fundamental principle of thermodynamics: phase change cooling.
- Low-Pressure Refrigerant Entry: Liquid refrigerant, which has been depressurized by the expansion valve, enters the evaporator at a low temperature and low pressure.
- Heat Absorption: As the vehicle's cabin air (which is warmer) is blown across the evaporator's fins by the blower motor, the heat from the air is absorbed by the cold refrigerant.
- Evaporation (Phase Change): This absorbed heat causes the liquid refrigerant to boil and transform into a low-pressure, cold gas (vapor). This is the "evaporation" process from which the component gets its name.
- Cool Air Delivery: As the air loses its heat to the refrigerant, it becomes cool and is then circulated back into the car's interior, providing that refreshing chill.
- Refrigerant Exit: The now gaseous refrigerant exits the evaporator and travels to the compressor to begin the cycle anew.
Essentially, the evaporator acts as the "cold coil" of your AC system, removing heat and humidity from the air inside your car.
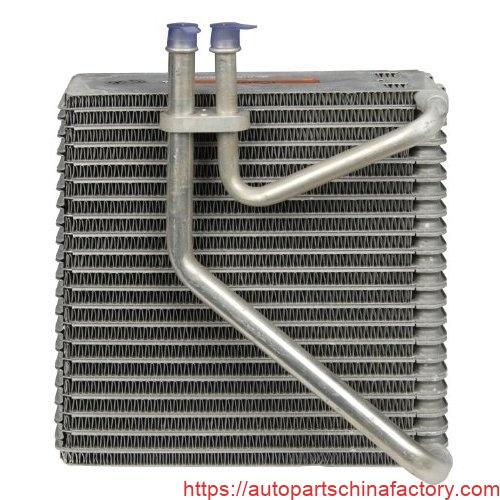

The Evaporator Supply Chain: From Raw Materials to Your Dashboard
The journey of an evaporator from raw materials to your car's dashboard involves a complex global supply chain:
- Raw Material Suppliers: Aluminum suppliers provide the base material for the fins and tubes.
- Component Manufacturers: Companies specialize in manufacturing the core components of the evaporator, often in highly automated facilities.
- Automotive Tier 1 Suppliers: Major automotive suppliers (like Denso, Mahle, Valeo, Sanden) integrate these components into complete AC modules or supply the evaporators directly to car manufacturers.
- Automotive OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers): Car manufacturers assemble these components into their vehicles.
- Aftermarket Distributors: For replacement parts, a network of distributors and retailers makes evaporators available to repair shops and consumers.
Leading Evaporator Manufacturers and Import Factories
Many global companies are at the forefront of evaporator manufacturing, often with factories strategically located around the world to serve major automotive production hubs. Some of the key players include:
- Denso: A leading global automotive supplier, Denso produces a wide range of AC components, including evaporators, with manufacturing facilities in various countries.
- Mahle GmbH: Another major international development partner and supplier to the automotive industry, Mahle is known for its thermal management products.
- Valeo: A French automotive supplier, Valeo designs and produces innovative systems for CO2 emission reduction and occupant comfort, including evaporators.
- Sanden Corporation: A Japanese manufacturer specializing in automotive air conditioning systems and components.
- Delphi Technologies (now BorgWarner Technologies): A significant player in automotive parts, including HVAC components.
- Behr Hella Service (joint venture between Mahle and Hella): Offers a comprehensive range of thermal management products for the aftermarket.
Import factories for these components are often found in countries with strong manufacturing capabilities and logistics networks, such as China, Mexico, various European nations, and parts of Southeast Asia. These facilities ensure a steady supply of evaporators to assembly plants worldwide.
Keeping Your Car Cool
The evaporator is a critical component for your driving comfort, especially during hot weather. Understanding its function and the sophisticated engineering behind it highlights the complexity of modern automotive systems. Regular AC maintenance, including checking for leaks and ensuring proper refrigerant levels, can help ensure your evaporator continues to provide efficient cooling for years to come.