- A+
Tube-fin radiators and Plate-fin radiators are two common types of heat exchangers, различаващи се значително по своята структура и типични приложения.
Tube-Fin Radiator
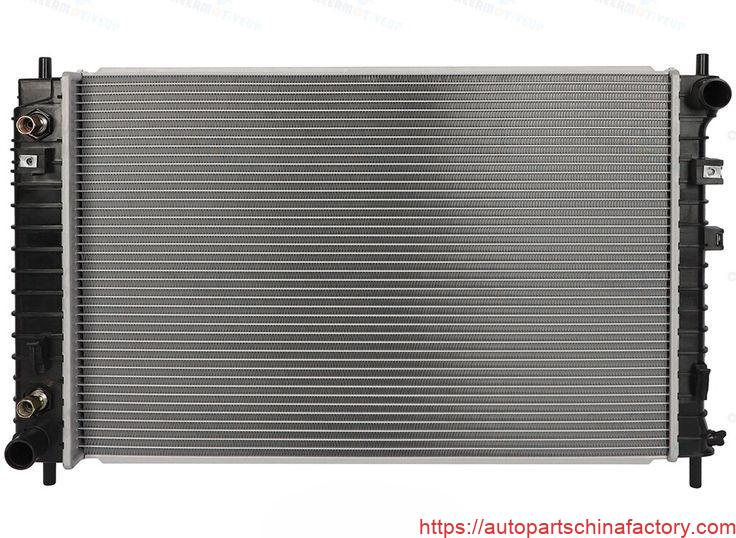

Structural Characteristics:
- Охлаждащи тръби: Основно се състои от сплескани охлаждащи тръби, през които тече охлаждащата течност.
- Топлинни разсейващи перки: Между охлаждащите тръби се поставят вълнообразни или сгънати перки, Увеличаване на повърхността на топлопреминаването.
- Резервоари: Обикновено има два резервоара (И двете страни или отгоре/отдолу) които свързват тръбите за охлаждане, Формиране на циркулационен път за охлаждащата течност.
- Материали: Често изработен от мед или алуминий, с компоненти, обединени заедно, използвайки спояване или подобни методи.
Принцип на работа:
Охлаждаща течност (such as water or antifreeze) flows through the cooling tubes, transferring heat to the tube walls. The tube walls then conduct this heat to the closely contacted fins. Air flows through the gaps between the fins, carrying away heat from the fins, thereby achieving heat dissipation.
Applications:
Tube-fin radiators are widely used in vehicles like cars, tractors, and construction machinery, representing a traditional form of automotive radiator.
Plate-Fin Radiator (often referred to as a Plate Heat Exchanger)

Structural Characteristics:
- Heat Transfer Plates: Consists of a series of parallel metal plates that form fluid channels between them.
- Fins: Between the plates, there are typically corrugated, straight, or serrated fins. These fins increase the heat exchange surface area and enhance heat transfer.
- Channels: Fluids flow through the channels formed by the plates and fins. Typically, hot and cold fluids are arranged alternately and do not mix.
- Sealing: The plates are sealed together using gaskets (e.g., rubber gaskets) or by brazing.
- Материали: Common materials include stainless steel, алуминий, Мед, and titanium, chosen based on the specific application's requirements for corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance.
Принцип на работа:
Hot and cold fluids flow in their respective independent channels, exchanging heat across the thin, large metal plates. The presence of fins further expands the heat transfer surface area and improves heat exchange efficiency. Due to the flexible design of the channels between the plates, various flow patterns like counter-flow and co-current flow can be achieved.
Applications:
Plate-fin radiators (more commonly known as plate heat exchangers) have extensive applications in industrial fields, включително:
- HVAC (Отопление, Вентилация, и климатик): Used for building heating, cooling, and hot water supply.
- Chemical Industry: For heating, cooling, condensation, and evaporation processes of various fluids.
- Food and Beverage: For pasteurization and cooling of products like milk and juice.
- Power Generation: For cooling generator sets.
- Pharmaceuticals: For temperature control in pharmaceutical production processes.
- Marine: For cooling marine engines.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | Tube-Fin Radiator | Plate-Fin Radiator |
| Structure | Cooling tubes (flat) and wavy heat dissipation fins | Parallel metal plates and various shapes of fins |
| Fluid Channels | Coolant in tubes, air between fins | Fluids in channels formed by plates and fins |
| Manufacturing | Typically brazing of tubes, fins, and tanks | Brazing, gasket sealing, or expansion joining of plates and fins |
| Characteristics | Relatively simple, lower cost, suitable for high flow, low pressure drop | Compact, high heat exchange efficiency, can withstand higher pressure, easy maintenance (some are detachable) |
| Applications | Automotive, tractor, construction machinery cooling | Industrial heating/cooling, HVAC, chemical, food, power |
| Maintenance | Usually replaced as a whole unit, difficult to disassemble for repair | Some types are detachable for cleaning or replacing plates/gaskets |
Export to Sheets
In essence, tube-fin radiators are primarily designed for heat dissipation via air convection, commonly used for cooling in mobile equipment like vehicles. In contrast, plate-fin radiators (plate heat exchangers) are focused on highly efficient heat exchange between two fluids, finding widespread use in industrial production and various thermal systems.